Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism
Drawing formulas from names. The S N 2 doesnt happen for secondary alcohols.

Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Youtube
Only one textbook in this admittedly incomplete sample mentions the S N i mechanism at all.
. The elements of water can be added to the doublebonded carbons of an alkene in either a Markovnikovs or an antiMarkovnikovs manner. Drawing formulas from names. Alkenes react with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form alcohols.
The antiMarkovnikovs addition results from a hydroborationoxidation reaction. C 4 H 8. There are 3 mechanisms suggested for the elimination reactions.
It is a subset of reactions that very closely resembles the insertion reactions and both are differentiated by the mechanism that leads to the resulting stereochemistry of the products. 3 CH 3 3 C-Br CN CH 3 2 CCH 2 Br HCN We know that t-butyl bromide is not expected to react by an S N 2 mechanism. Alkenes having four or more carbon atoms can form diverse structural isomersMost alkenes are also isomers of cycloalkanesAcyclic alkene structural isomers with only one double bond follow.
Drawing alcohol formulas. Preparation of alkenes consists of the _____ of alkyl halides with a _____ base via an _____ mechanism. Formation of alkenes.
Drawing alkyne formulas from names. As shown in the following figure a hydrogen ion catalyzes the Markovnikovs addition. Products 214 to 215.
A recent application is the generation of highly reactive aryl radicals which are useful arylating reagents in synthesis by photoinduced electron transfer PET from photoredox catalysts to suitable precursors followed by bond scission 8 9However the choice of aryl radical precursors is currently limited to electron-poor arenes such as diazonium 6 10 or. 1-butene 2-butene and isobutylene. From alkenes i By acid catalysed hydration.
CHCl COEt ACN CoEt AcOEt CN -78C 8h 25 75 When cyclopentadiene is added in excess the reaction is pseudo-1 order with respect to the fumaric nitrile ester. C 5 H 10. C 2 H 4.
However often the two are used interchangeably because the. Alcohol dehydration is an example of an elimination reaction which is quite the opposite of substitution reaction and addition. A catalyst containing atomically dispersed Pd sites on N-heterocyclic carbene NHC-stabilized Au nanoclusters with the precise formula of PdAu 9 NHC Bn 7 X 2 NHC Bn is dibenzylbenzimidazolin-2-ylidene X is Br or Cl has been developed for the regioselective hydrogenation of alkenes.
Matching alcohols to their names I. Furthermore the ethanol solvent is not. You will find it - Its all here.
1212 Structure of the Carbonyl. C 3 H 6. Preparation of Hydrocarbons Alkenes.
Theres no warning sign saying wait. In addition to primary amines secondary amines led to reductive coupling with nitriles and provided tertiary chiral amines in up to 85 yields and 99 ee Fig. Mechanism The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps.
In four textbooks where SOCl 2 is mentioned the reaction is shown as proceeding through an S N 2 mechanism. We have not yet considered the factors that influence elimination reactions such as example 3 in the group presented at the beginning of this section. Two vicinal.
Most of the reactions involving the preparation of alkenes involve elimination process. The bond angles are approximately 120 as expected of a trigonal coplanar structure Figure 121. Which of the following options correctly describe the addition of a hydrogen halide to an.
Represented by R-Mg-X where R is an alkyl or aryl group while X is a halogen the Grignard reagent easily forms a carbon-carbon bond of 1 2. Notably for products 210 and 214 12 to 14 racemization is observed which can be explained by the comparably high acidity of the α-hydrogen atom in the case of the starting 2. Organic Chemistry Study Materials Practice Problems Summary Sheet Guides Multiple-Choice Quizzes.
Each Pd site is encircled by an Au 9 ring protected by seven NHC. Drawing alkene formulas from names. All these eliminations are β- eliminations.
Thus the carbonyl carbon and the three atoms attached to it lie in the same plane and the π-electron cloud is above and below this plane. C n H 2n. The following Diels-Alder cycloaddition was recently performed by Mukherjee et al.
Drawing formulas from names. A migratory insertion is a type of reaction in organometallic chemistry wherein two ligands on a metal complex combine. In case of unsymmetrical alkenes the addition reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikovs rule Unit 13 Class XI.
Is a halogen atom that has a negative charge. In addition the oxygen atom also has two non bonding electron pairs. Hydration of alkenes follows a similar mechanism to hydrohalogenation however the water must be deprotonated in the final.
This makes alcohols and ethers less reactive than the alkyl halides compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms in an. Reaction Mechanism Click Here for Sample Questions The haloalkanes or aryl halides with sp 3 or sp 2 hybridised carbon atoms when reacted with Magnesium metal give Grignard reagent which is an organometallic compound.

Electrophilic Addition Reactions Of Alkenes Mcc Organic Chemistry
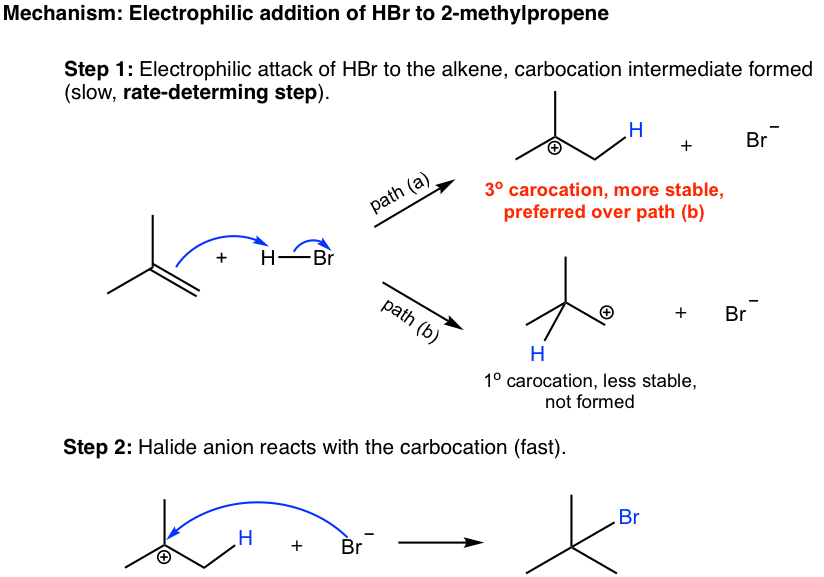
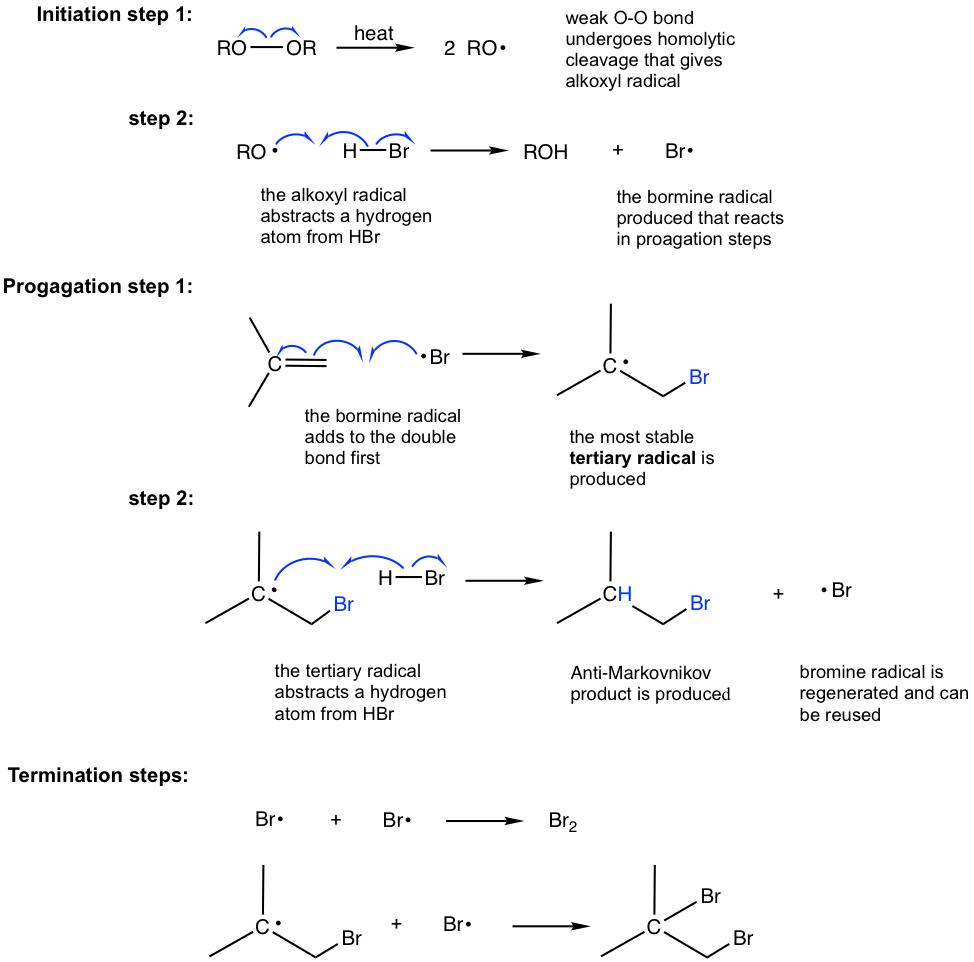
10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Alkenes Chemgapedia
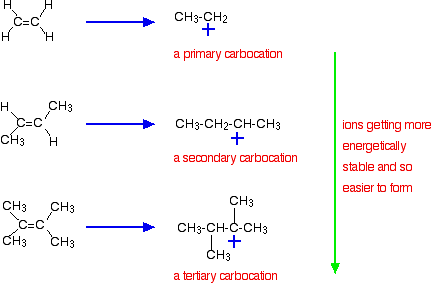
9 2 Addition Of Hydrogen Halides To Symmetrical Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
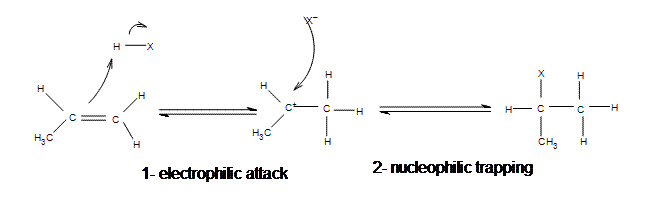
Electrophilic Addition Of Hydrogen Halides Chemistry Libretexts

10 2 Reactions Of Alkenes Addition Of Hydrogen Halide To Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
0 Response to "Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes Mechanism"
Post a Comment